Cyst Removal Surgery: Cost, Benefits, Procedure & Recovery Explained

Cyst removal surgery is a minor or major medical procedure aimed at extracting abnormal fluid-filled sacs, known as cysts, from various parts of the body. These can range from small skin cysts to deeper internal ones. Timely removal is crucial to prevent infection, rupture, or discomfort. Common cyst types removed surgically include sebaceous, ganglion, ovarian, and pilar cysts. Whether for cosmetic concerns or medical necessity, understanding this procedure helps patients make informed choices.
Understanding What a Cyst Is
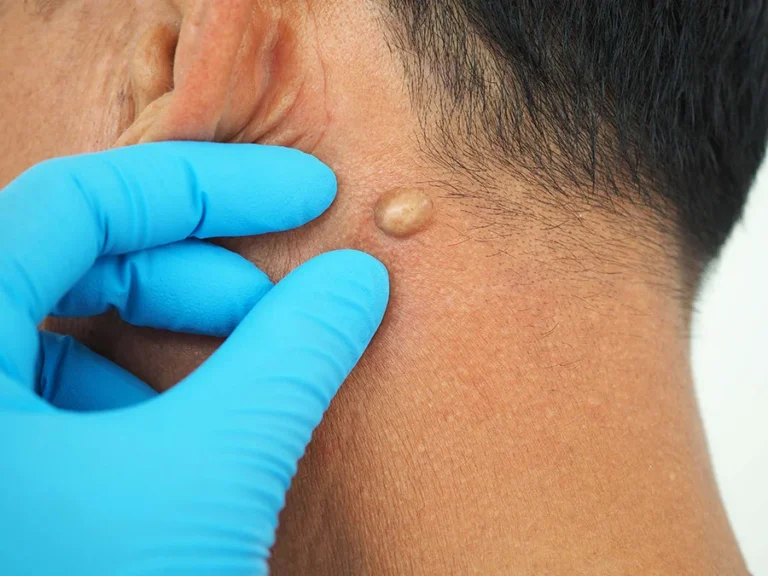
A cyst is a closed sac-like structure filled with fluid, air, or other substances. These can appear anywhere—on the skin, scalp, ovaries, or breasts. Often harmless, cysts can result from infections, blocked glands, or chronic inflammation. While many disappear naturally, some persist or grow, requiring medical attention. Identifying their cause early helps determine whether observation or intervention is the right path.
When Is Cyst Removal Surgery Needed?
- Medical reasons: Pain, infection, rupture, or pressure on surrounding tissues.
- Cosmetic concerns: Visible or growing cysts that affect confidence or appearance.
- Warning signs: Redness, swelling, tenderness, fluid discharge, or rapid growth.
- Delaying removal: Can increase risk of infection, scarring, or more complex surgery later.
Types of Cysts That May Need Removal
Several cyst types commonly require removal including:-
- Sebaceous cysts: Common on the face, neck, and back; often filled with keratin.
- Ovarian cysts: Develop on ovaries; may cause abdominal pain or fertility issues.
- Ganglion cysts: Found near joints or tendons, especially in the wrists or hands.
- Baker’s cysts: Fluid-filled cysts behind the knee, often linked to joint problems.
- Pilar (scalp) cysts: Typically painless, but can grow and become inflamed.
- Breast cysts: Can mimic lumps and are often removed for biopsy or relief.
Diagnosis and Evaluation Before Surgery
Diagnosis Before Cyst Surgery: A specialist consultation is the first step. The doctor may conduct a physical examination followed by imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI. In some cases, a biopsy is required to rule out malignancy. The goal is to understand the cyst’s type, size, depth, and whether surgery is the best course. This evaluation is vital in creating a safe and effective treatment plan.
Preparation Before the Surgery
Patients receive pre-operative instructions including avoiding food or drink before surgery, stopping certain medications, and maintaining hygiene. Blood tests or scans may be scheduled beforehand. On the day, arrive early, wear comfortable clothing, and have a support person if sedation is planned. Being well-prepared reduces anxiety and enhances surgical outcomes for patients undergoing cyst removal in Newcastle.
Different Types of Cyst Removal Procedures
- Excision surgery: Full surgical removal of the cyst and its sac; reduces recurrence.
- Laparoscopic removal: Minimally invasive option for internal cysts like ovarian.
- Laser removal: Suitable for some superficial skin cysts with minimal scarring.
- Needle aspiration: Draws fluid out but may not prevent recurrence without sac removal.
- Surgical excision vs. aspiration: Surgery offers a more permanent solution.
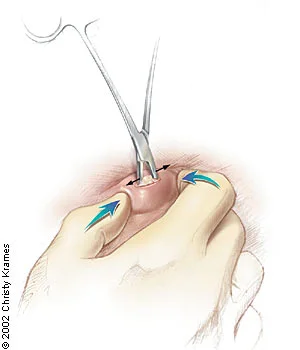
Step-by-Step: How Cyst Removal Surgery Is Done
Depending on the cyst’s location, local or general anaesthesia is used. The surgeon makes an incision, taking out a cyst and its sac, and closes the wound with sutures. The process can take 15 minutes to over an hour. For deep or complex cases like ovarian cysts, laparoscopic techniques might be used. Procedures like sebaceous cyst removal in Newcastle are often quick and done in-clinic.
Cyst Removal Surgery Cost
The cost varies based on the cyst type, location, complexity, and whether it’s done privately or through the NHS. Clinics in the UK may charge anywhere from £250 to £800 for minor removals. In India, costs are generally lower. Some insurance plans cover removal if it’s deemed medically necessary. It’s advisable to verify with the clinic offering cyst removal in Newcastle upon Tyne services.
Benefits of Undergoing Cyst Removal Surgery
- Prevents infection: Stops cysts from rupturing or becoming inflamed.
- Boosts confidence: Especially for cysts in visible or bothersome locations.
- Reduces recurrence: Removal of the entire sac lowers chances of return.
- Enables diagnosis: Excised cysts can be biopsied for accurate analysis.
Risks and Complications of Cyst Removal Surgery
Like all surgeries, this procedure carries some risk—bleeding, infection, and scarring are the most common. Rarely, cysts may recur if not fully removed. Proper wound care and following medical advice can help minimise issues. Always contact your doctor if you notice signs of infection, prolonged pain, or discharge from the surgical site during recovery.
Recovery and Aftercare Instructions
- Wound care: Keep the area clean, dry, and follow dressing guidelines.
- Pain management: Mild discomfort managed with prescribed or over-the-counter meds.
- Healing timeline: Most wounds heal within 1–2 weeks; scarring fades over time.
- Follow-up care: Attend scheduled check-ups and suture removal if required.
- Limit activity: Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous movements until fully healed.
Lifestyle Tips to Support Healing and Prevent Recurrence
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins to support tissue repair. Stay hydrated and avoid smoking. Maintain hygiene, especially around the surgical site, to prevent infection. For skin cysts, avoid using oily or comedogenic products. Gradually reintroduce physical activities as advised by your doctor to ensure the wound heals properly.
Choosing the Right Surgeon or Clinic
Look for a clinic registered with the Care Quality Commission (CQC) and a surgeon with relevant experience. Board certification in plastic or general surgery is key. Reading patient testimonials and viewing before-after photos helps evaluate quality. Trust your instincts—choose a team that communicates clearly and provides personalised care.
Myths and Facts About Cyst Removal Surgery
Contrary to popular belief, cysts do not always grow back—especially if the sac is fully removed. Most procedures are quick and done under local anaesthesia, with minimal discomfort. Not all cysts need surgery; however, ignoring problematic ones can lead to complications. Educating yourself with facts helps you make confident healthcare decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is cyst removal surgery painful?
Mild discomfort is possible, but local anaesthesia prevents pain during the procedure.
How long does the procedure take? Most cysts can be removed in 20–60 minutes, depending on complexity.
Will there be a visible scar after the surgery? A small scar may form, but proper care and expert techniques minimise its appearance.
Is hospitalisation required? Not usually—most cases are done as outpatient procedures.
Can I go to work after the surgery? Yes, often within a day or two, unless advised otherwise by your surgeon.