![Batch DOC and DOCX Converter Cracked Patch x86-x64 [Stable] 2025](https://eldonaesthetics.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/image00006.jpg)
1. Introduction to Cyst Removal
1.1 What Is a Cyst?
What is a cyst? It is a closed sac-like structure that can appear under the skin or in deeper tissues, filled with fluid, air, or other material. It can develop due to infection, blocked glands, or chronic inflammation. Though usually benign, proper diagnosis and safe removal are crucial, especially when the cyst becomes painful or inflamed.
1.2 Common Types of Cysts
Cysts come in various forms—sebaceous, epidermoid, ganglion, and pilar cysts are among the most common. Their locations vary, including the scalp, back, hands, and face. Understanding the cyst type helps in planning the most effective and safe treatment or surgical approach.
1.3 Why Safe Removal Is Important
Improper or delayed cyst treatment can lead to infection, scarring, or even misdiagnosis of more serious conditions. Cyst removal surgery ensures complete extraction, reduces recurrence risk, and allows for histological testing, making it the safest and most effective option.
2. Causes and Symptoms of Cysts
2.1 Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, like acne, PCOS, or genetic syndromes, can trigger cyst development. Sebaceous glands, when blocked, are especially prone to forming cysts, often requiring clinical attention.
2.2 Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Poor hygiene, repetitive skin trauma, and even stress can contribute to cyst formation. Inadequate skincare or wearing tight clothing that irritates hair follicles may also increase risk.
2.3 Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Cysts that rapidly grow, become painful, change color, or ooze should be evaluated by a professional. Early intervention avoids complications and ensures proper care through methods like cyst removal surgery.
3. Diagnosis Before Removal
3.1 Physical Examination
Most cysts are diagnosed by physical appearance. Your doctor will assess its size, location, and consistency. If infected, surrounding tissue inflammation may also be noted.
3.2 Imaging and Lab Tests
Ultrasound or MRI may be used to determine the cyst’s depth and structure. In some cases, a biopsy might be needed to rule out malignancy, especially if the cyst recurs or behaves abnormally.
3.3 Differentiating Between Benign and Serious Conditions
Benign cysts grow slowly and are usually painless. In contrast, aggressive or cancerous masses tend to grow rapidly and may invade surrounding tissue. Accurate diagnosis is critical to ensure appropriate treatment.
4. Safe Medical Removal Methods
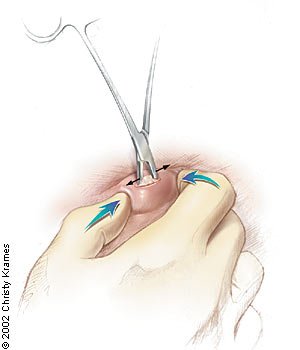
4.1 Surgical Excision
This is the most reliable method of cyst removal surgery. The entire cyst, including its sac, is surgically removed, reducing the chance of recurrence. It’s usually performed under local anaesthesia.
4.2 Needle Aspiration
In this method, fluid is drawn out using a syringe. While less invasive, it doesn’t remove the cyst wall, which can result in recurrence. It’s typically used for temporary relief or diagnosis.
4.3 Laser Removal
Laser treatment may be used for small, superficial cysts. It offers minimal scarring and faster healing, though it’s not suitable for deep or large cysts.
4.4 Cryotherapy Techniques
Cryotherapy uses extreme cold to destroy cyst tissue. Though effective for some skin lesions, it’s not commonly used for deeper or complex cysts like those treated in a proper clinical setting.
5. Why Avoid DIY Cyst Removal
5.1 Infection Risks
Attempting to pop or drain a cyst at home can introduce bacteria and lead to serious infections, requiring further medical intervention and antibiotics.
5.2 Potential Scarring and Tissue Damage
Untrained removal efforts can damage surrounding skin, nerves, or blood vessels. Scarring is also more likely without sterile technique and proper wound care.
5.3 Risk of Misdiagnosis
Mistaking a cyst for a boil, abscess, or tumour could delay essential treatment. Only a medical professional can offer accurate diagnosis and safe removal options like those provided at cyst removal Newcastle clinics.
6. Preparing for Cyst Removal
6.1 Pre-Procedure Consultation
During consultation, the surgeon will evaluate the cyst, discuss your medical history, and explain the most suitable removal method. This is also the time to ask questions.
6.2 Medical History and Precautions
Inform your provider about allergies, medications, or past procedures. These factors help prevent complications during and after the cyst removal surgery.
6.3 Patient Preparation Checklist
Shower on the day of surgery, avoid applying creams near the cyst, and follow fasting instructions if advised. Wear comfortable clothing and arrange transportation if sedation is used.
7. The Removal Procedure – Step-by-Step
7.1 Anesthesia Administration
Local anaesthesia is administered to numb the area. For larger or multiple cysts, mild sedation may be used. The procedure is usually painless.
7.2 Incision and Extraction Process
A small cut is made over the cyst, and the entire sac is removed. The goal is complete extraction to prevent recurrence, especially in sebaceous cyst removal Newcastle procedures.
7.3 Wound Cleaning and Closure
After removal, the wound is cleaned and stitched or dressed. You may receive antibiotic ointment to apply at home, and detailed aftercare instructions are provided.
8. Recovery and Aftercare
8.1 Healing Timeline
Most patients recover within 7 to 14 days, depending on the cyst’s size and location. Scabs form and fall off as the wound heals.
8.2 Pain Management and Medications
Pain is usually mild and controlled with OTC pain relievers. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection. Follow dosage instructions carefully.
8.3 Caring for Stitches or Dressings
Keep the area clean and dry. Change dressings as advised and avoid scratching or applying pressure to the site. This helps prevent infection and supports smooth healing.
9. Risks and Complications
9.1 Infection and Recurrence
Infections can occur if aftercare is neglected. Also, if the cyst sac isn’t fully removed, it may come back—underscoring the need for expert treatment like cyst removal Newcastle upon Tyne services.
9.2 Allergic Reactions
Rarely, patients may react to anaesthesia or medications. Always inform your provider about any allergies during consultation.
9.3 Long-Term Skin Changes
There may be slight discolouration or scarring. Using silicone gel or prescribed creams can help minimise these effects over time.
Conclusion
Cyst removal surgery is the safest and most effective way to treat troublesome or recurring cysts. Avoid DIY methods, follow proper recovery steps, and consult certified specialists for best outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can a cyst go away without removal?
Some small cysts may shrink, but most require removal to prevent recurrence.
How painful is the procedure?
The procedure is minimally painful, thanks to local anaesthesia.
Is cyst removal covered by insurance?
If medically necessary, yes. Cosmetic removals might not be covered.
Can the cyst come back after removal?
Yes, if the entire sac isn’t removed. Surgical excision helps reduce this risk.
What’s the difference between a cyst and an abscess?
A cyst is a non-infectious sac; an abscess is pus-filled and typically infected.




One thought on “Taking Out a Cyst: Safe Methods, Risks & Recovery Tips”